Hydrolysis subsequently causes flake formation and flakes can be removed by sand filtration. Stability and structure of carbocations.
Other Oxidation Reduction Reactions
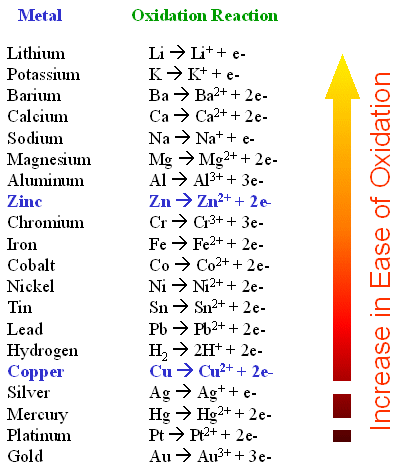
Oxidation occurs when a chemical species loses or gives up electrons to another chemical species.
Iron chloride and tin oxidation reaction. Leaching is a process of 1 Silica 1 Reduction 2 Concentration 3 Refining 4 Oxidation 22. Iron removal from wastewater may be achieved by oxidation of binary iron to tertiary iron. This is done by dipping the iron into molten tin or by electroplating an iron sheet using tinIV chloride as the electrolyte.
IronIII oxide aluminium aluminium oxide iron. Simple S N 2 reaction. Metals in the fourth class are so unreactive they are essentially inert at room temperature.
Once underway the reaction is highly exothermic rapidly reaching temperatures as high as 2000 C well in excess of the melting point of iron 1535 C. When metallic iron oxidation state 0 is placed in a solution of hydrochloric acid ironII chloride is formed with release of hydrogen gas by the reaction Fe 0 2 H Fe 2 H 2. 2 o Benzyl Chloride with HS S N 2 Mechanism.
The cans do not rust as long as the tin coating remains. Valency 1 Valency 2 Valency 3. A redox reaction is the simultaneous occurrence of the two components or half reactions.
The periodic table is a tabular display of the chemical elements organized on the basis of their atomic numbers electron configurations and chemical properties. Benzyl Chloride with HS S N 2 Reaction. The familiar form white or beta tin and gray or alpha tin which is powdery and of little use.
Redox Reaction is a chemical reaction in which oxidation and reduction occurs simultaneously and the substance which gains electrons is termed as oxidizing agent. To be sure reaction was complete small excess of the SnCl 2 is added and then solution is treated with mercury II chloride. There is enough hydrogen and oxygen in the air to allow the atoms to bond with the iron.
Thus vanadium forms. When iron metal is exposed to air and water usually it turns into rust a. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 Redox Reactions Redox Reactions is the eighth chapter in the NCERT Class 11 Chemistry textbookThis chapter is regarded by many as one of the most important chapters in the term I CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus 2021-22 owing to the fact that the entire field of electrochemistry deals with redox reactions.
After tin plating the inside of the can is coated with a thin layer of plastic. Since the process of oxidation-reduction involves the addition and removal of atoms and charges writing a balanced chemical equation for such reactions is quite a daunting task. S N 2 examples.
Weve all noticed reddish-brown rust on iron nails. Oxidation may be achieved by adding oxygen or other oxidants such as chlorine or potassium permanganate. Redox calculator is an online tool which you can use for free.
The oxidation process provides the electrons necessary for reduction to occur. But thanks to the redox reaction calculator which makes it easier for students and researchers to balance a complicated redox equation in just a second. Possible oxidation states are 23.
S N 1 and S N 2. Refer the following table which gives you oxidation numbers. Electron configuration of Iron is Ar 3d6 4s2.
The practical use of this reaction is to weld railway lines together and could be mentioned. Tin exists in two different forms or allotropes. Allyl Chloride with HS S N 2 Reaction.
It also contains even less active metals such as copper which only dissolves when treated with acids that can oxidize the metal. Ca 2 Iron III. The products of reaction with chlorine usually are chlorides with high oxidation numbers such as iron trichloride FeCl 3 tin tetrachloride SnCl 4 or antimony pentachloride SbCl 5 but it should be noted that the chloride of highest oxidation number of a particular element is frequently in a lower oxidation state than the fluoride with the highest oxidation number.
Reduction occurs when a chemical species receives or gain electrons. Tin is a chemical element with atomic number. Fe 0 Cu 2 Fe 2 Cu 0.
This shows that aluminium is above iron in the reactivity series. Concentration of copper pyrites is done by - 1 Gravity separation 2 Froath floatation process 3 Electromagnetic separation. S N 2 Reaction.
Iron metal is more electropositive than copper and therefore will displace it from its salts. Rust is largely hydrated iron III oxide Fe 2 O 3xH 2 O as a result. During rusting iron combines with oxygen in the air in the presence of water to generate Fe 2 O 3xH 2 O a hydrated iron III oxide.
It is when moisture is added that the oxidation process starts to occur. The reaction rate. 3 Chloride ores 4 None of these as impurity 21.
Iron is present in all wastewaters. This creates the chemical reaction known as oxidation or rust. Table of Common Ions.
The low melting point of tin and its firm adhesion to clean surfaces of iron steel copper and copper alloys facilitate its use as an oxidation-resistant coating material. Tin plating is usually used for making tin cans as tin is very expensive. 2FeCl 3 SnCl 2 2FeCl 2 SnCl 4.
Substrate structure controls substitution mechanism S N 1 or S N 2. The gray form changes to the white above 132 C 558 F rapidly. TinII chloride also known as stannous chloride is a white crystalline solid with the formula The template Tin is being considered for deletion Sn The template Chlorine is being considered for deletion Cl 2It forms a stable dihydrate but aqueous solutions tend to undergo hydrolysis particularly if hotSnCl 2 is widely used as a reducing agent in acid solution and in.
The third class contains metals such as chromium iron tin and lead which react only with strong acids. The tin provides a protective oxide coating to the cans. It is possible to reduce iron 3 using Jones reductor column filled with granules of amalgamated zinc however most commonly reduction is done with tin II chloride.
Iron rusting is an oxidation reaction. This hydrated iron Ill oxide is referred to as rust. Therefore the oxidized species is the reducing agent and.
These metals are ideal for making jewelry or coins because they do. Because the air we breathe has moisture in it oxidation will occur even if there is no water added to the metal. The colour of rust is reddish-brown.
Electron Configuration and Oxidation States of Iron.
Causes Chemistry Of Rusting Rust Prevention Introduction To Oxidation Reduction Redox Reactions Gcse Igcse Ks4 Science Chemistry Revision Notes Revising

Oxidation Reduction Reaction Half Reactions Britannica
Causes Chemistry Of Rusting Rust Prevention Introduction To Oxidation Reduction Redox Reactions Gcse Igcse Ks4 Science Chemistry Revision Notes Revising
Causes Chemistry Of Rusting Rust Prevention Introduction To Oxidation Reduction Redox Reactions Gcse Igcse Ks4 Science Chemistry Revision Notes Revising

Redox Reaction Oxidation Of Iron Ii To Iron Iii Redox Equilibrium Youtube
Causes Chemistry Of Rusting Rust Prevention Introduction To Oxidation Reduction Redox Reactions Gcse Igcse Ks4 Science Chemistry Revision Notes Revising
Causes Chemistry Of Rusting Rust Prevention Introduction To Oxidation Reduction Redox Reactions Gcse Igcse Ks4 Science Chemistry Revision Notes Revising
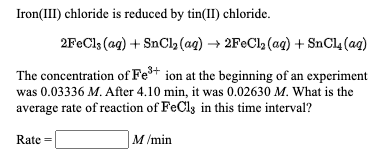
Answered Iron Iii Chloride Is Reduced By Bartleby

Iron Transition Metal Chemistry Iron Ii Fe2 Iron Iii Fe3 Complexes Ions Ligand Substitution Redox Chemical Reactions Principal Oxidation States 2 3 Extraction Gce As A2 Ib A Level Inorganic Chemistry Revision Notes