The National Cancer Institute standardized response criteria regarding changes in enhanced lesion size on T1-weighted MR images were used to define treatment response. The toxicity profiles were mild.
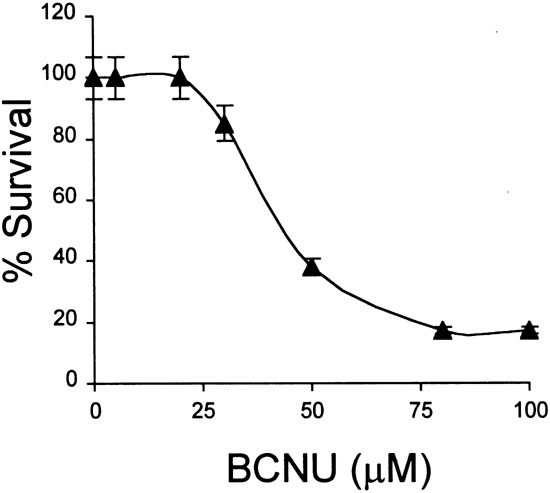
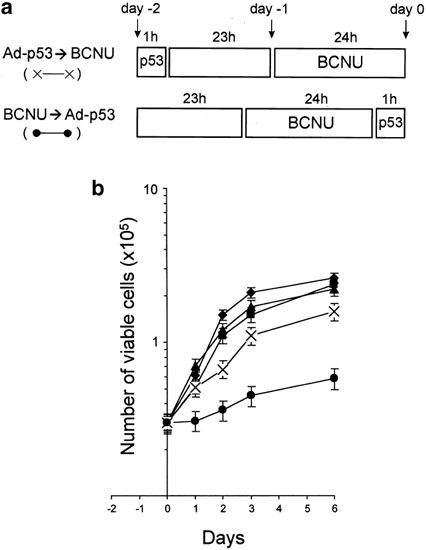
Increase Of Bcnu Sensitivity By Wt P53 Gene Therapy In Glioblastoma Lines Depends On The Administration Schedule Gene Therapy
950 of the patients in the 300 mg group and all patients in the 400 mg group experienced at least one AE relating to the treatment.
Define bcnu treatment. Treatments are often used in combination with one another. Rituximab 375 mgm 2 dose IV. Grade 3 toxicities were reported for fatigue anemia and diarrhea in more than one patient.
Treatment options vary depending on the type grade size and location of the tumor. A cooperative clinical trial. 6 Preemptive treatment at molecular relapse if relapse occurs.
Treatment-related grade 34 AEs including hyperglycaemia nausea diarrhoea and vomiting occurred in 727 patients at 400 mg and 400 patients at 300 mg. Whether it has spread. La incidencia de anemia en el paciente en tratamiento quimioterápico va a depender de diversos factores tales como el tipo y dosis de.
Se define como una disminución de los niveles de hemoglobina Hb por debajo de 12 gdl. BRCA testing which was undertaken after treatment revealed that 7 patients with unknown BRCA status prior to enrollment had BRCA mutations with 43 37 responses seen whereas the remaining 46 patients negative for BRCA mutation had a response rate of 239. El glioblastoma también conocido como glioblastoma multiforme o con las siglas GBM es el tumor más común y más maligno entre las neoplasias de la glíaSu nombre quedó establecido por la clasificación OMS-2000 2 y fijado por la clasificación OMS-2007.
An employee in the performance of official duties gives preferential treatment to an individual corporation or organization including a non-profit organization in which the employee or a relative or friend of the employee has an interest financial or otherwise. These alterations define molecular classes that are associated with metastatic risk. Evaluation of BCNU andor radiotherapy in the treatment of anaplastic gliomas.
Infusion once weekly x 4 doses. In these guidelines we define the role of the major treatment modalities of surgery radiotherapy and systemic pharmacotherapy covering current advances and cognizant that unnecessary interventions and expenses should be avoided. Early exposure to common infections in early childhood appears to decrease the risk of Hodgkin lymphoma most likely by maturation of cellular immunity78More males than females are affected in the youngest.
The goal of treatment may be curative or focus on relieving symptoms palliative care. Individuals aged 14 years and younger have a higher prevalence of nodular lymphocyte-predominant disease and Epstein-Barr virus EBVassociated mixed-cellularity disease. Surgery alone or in combination with another local treatmentsuch as transarterial embolization selective internal radiotherapy isolated hepatic perfusion hepatic artery infusion and immune-embolizationhas been employed with benefit in terms of prolonged survival only in selected patients.
PCR is a test performed on blood or bone marrow cells that is used to detect a very small number of cancer cells with. Aproximadamente un 75 de los pacientes con cáncer en tratamiento quimio o radioterápico presentan anemia moderada con cifras de hemoglobina entre 12 y 8 gdl. The goal is to remove all or as much of the tumor as possible through surgery to minimize the chance of.
An employee benefits from or is reasonably perceived by the public to have benefited from the use of information acquired. Em sua maioria as combilexinas apresentam um mecanismo de ação predominante onde ora o intercalante maior afinidade pelas bases CG ora o ligante na fenda menor maior afinidade pelas bases AT define a afinidade do híbrido pelo B-DNA. A cooperative clinical trial.
Experimental Hematology publishes original research reports regular and fast-track submissions reviews letters to the editor and abstracts of the annual meeting of ISEH - International Society for Experimental HematologyWe welcome manuscripts describing basic in vitro and in vivo research centered on normal and malignant hematopoiesis as well as non-malignant hematologic. 3 De acuerdo con esta clasificación de la OMS de los tumores del sistema nervioso central el nombre genérico para este tumor. Molecular detection of relapse involves a specific test known as polymerase chain reaction or PCR.
Não é bem compreendido o comportamento deste fenômeno entretanto sabe-se que a afinidade pode estar relacionada à estabilidade e às condições de. This document is intended to be a source of reference for professionals involved in the management of adult patients with diffuse gliomas for patients and. And your age and general health.
Academiaedu is a platform for academics to share research papers. In brief a CR was defined as the complete disappearance of all evidence of lymphoma partial response PR as a 50 decrease in tumor size PD as a 25 increase in tumor size or the appearance of any new.
Radioactivity is a phenomenon exhibited by a few matters of emitting energy and subatomic particles spontaneously. Radioactive decay is a property of several naturally occurring elements as well as of artificially produced isotopes of the elements.

Ssc Exams Non Technical Phenomenon Of Radioactivity In Hindi Offered By Unacademy
Radioactivity in Chemistry means the same thing as it means in Physics or any other field of science.

Define radioactivity in chemistry. All radioactive isotopes release radiation but not all radiation comes from radioactivity. The substances which emit such kind of radiations are known as radioactive elements the phenomenon is termed as radioactivity. Further investigations showed that the radiation was a combination of particles and electromagnetic rays with its source being the atomic nucleus.
Atoms of uranium and plutonium are naturally radioactive atoms. There are three main forms of radioactive emissions. Radioactive isotopes have an unstable nucleus that decays or emits excess energy or radiation until the nucleus becomes stable.
Radioactivity refers to the decay or splitting of an atomic nucleus. Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of nucleus of an atom in which invisible radiations are emitted from the nucleus of atoms. Because the nucleus experiences the intense conflict between the two strongest forces in nature it should not be surprising that there are many nuclear isotopes which are unstable and emit some kind of radiation.
Radioactive Decay to other Elements When isotopes decay they can lose some of their atomic particles ie. Six types of radiation produced during nuclear. They can be naturally occurring or artificial isotopes of.
It is in essence an attribute of individual atomic nuclei. Definition of radiation chemistry. 6 neutrons 13 protons.
Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus and provide most of the mass of an atom while electrons circle the nucleus in shells and. The most common radioactive atoms have high atomic numbers and contain a large excess of neutrons. The Discovery of Radioactivity.
Radioactivity involves the spontaneous emission of material andor energy from the nucleus of an atom. Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of particles and electromagnetic radiation from nuclei of unstable atoms. Chemistry that deals with the chemical effects of nuclear and other radiations on matter.
Radioactivity property exhibited by certain types of matter of emitting energy and subatomic particles spontaneously. These radiations are emitted by an atomic nucleus that for some reason is unstable. Radioactivity definition is - the property possessed by some elements such as uranium or isotopes such as carbon 14 of spontaneously emitting energetic particles such as electrons or alpha particles by the disintegration of their atomic nuclei.
An alpha particle is composed of two protons and two neutrons and. The first is called an alpha particle which is symbolized by the Greek letter α. Radioactivity is caused when atoms in objects lose particles and emit high-energy radiation.
Radioactivity is due to the nuclear instability of an atom. Radioactive decay also known as nuclear decay radioactivity radioactive disintegration or nuclear disintegration is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiationA material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactiveThree of the most common types of decay are alpha decay 𝛼-decay beta decay 𝛽-decay and gamma decay 𝛾-decay all of which. We saw in Chapter 3 Atoms Molecules and Ions that atoms are composed of subatomic particlesprotons neutrons and electrons.
Scientists use radioactive atoms or isotopes in objects for many technologies and medicines. Electrons and protons and turn from one element into another. Sometimes isotopes decay from one unstable isotope into another unstable isotope.
Radioactivity refers to the particles which are emitted from nuclei as a result of nuclear instability. Radioactivity definition the phenomenon exhibited by and being a property of certain elements of spontaneously emitting radiation resulting from changes in. Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of particles and radiation from atomic nuclei.
It is the decomposition of unstable atomic nuclei and thus the energy that is released is called radioactive decay. The most common types of radiation are called alpha beta and gamma radiation. This can happen continuously in.
Examples of decay include alpha decay beta decay gamma decay neutron release and spontaneous fission. These emanations were ultimately called radioactivity. Radioactivity is the radiation that is released from an unstable atomic nucleus.
As the name implies radioactivity is the act of emitting radiations spontaneously. A radioactive material releases radiation when it decays. Radioactivity is defined as the emission of particles and electromagnetic rays from the nucleus of an unstable atom.
A radioactive process in which a nucleus undergoes spontaneous transformation into one or more different nuclei and simultaneously emits radiation loses electrons or undergoes fission. Define and give examples of the major types of radioactivity.