Pharmacokinetics of a drug depends on patient-related factors as well as on the drugs chemical properties. See also Overview of Pharmacokinetics Overview of Pharmacokinetics Pharmacokinetics sometimes described as what the body does to a drug refers to the movement of drug into through and out of the bodythe time course of its absorption bioavailability distribution.

Variability In The Responsiveness To Low Dose Aspirin Pharmacological And Disease Related Mechanisms
Age-related slowing of gastrointestinal motility or use of anticholinergic drugs can prolong movement of drugs through the stomach to the small intestine.
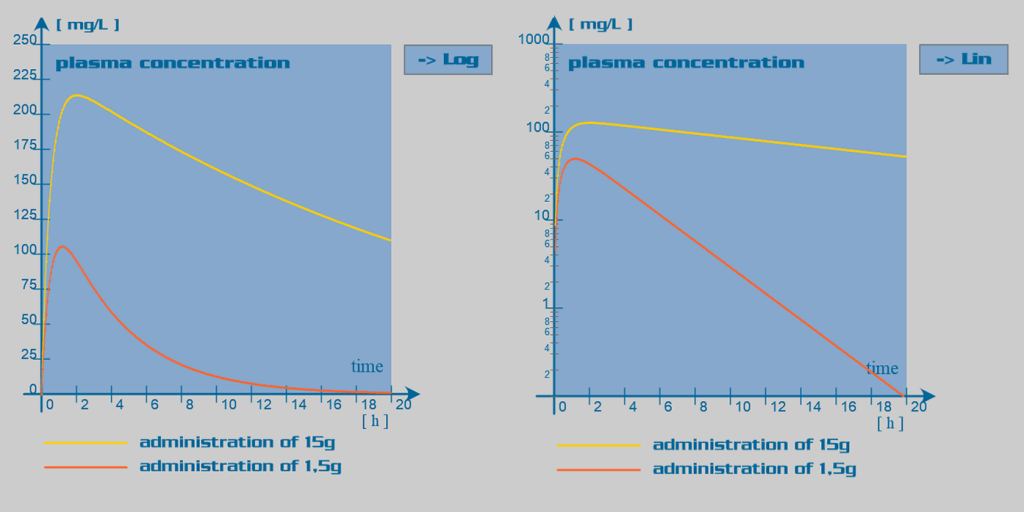
Pharmacokinetics of aspirin. Aspirin also known as acetylsalicylic acid ASA is a medication used to reduce pain fever or inflammation. Alright so once the medication is administered it first has to be absorbed into the circulation then distributed to various tissues throughout the body metabolized or broken down and finally eliminated or excreted in the. Read more Causes of low bioavailability.
The following processes govern the rate of accumulation and removal of drug from an organism absorption distribution metabolism and excretion. Salicylate is the active metabolite responsible for most anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects but acetylsalicylate is the active moiety for the antiplatelet-aggregating effect. For example the half-life of some drugs especially those that require.
We summarize the sex differences that impact pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics and include a general comparison of clinical pharmacology as it applies to men pregnant and non-pregnant women. The rate of metabolism andor elimination is directl y proportional to the plasma concentration of the drug C p decreases exponentially over time First-order is a flow-dependent. It is taken by mouth.
Since this is an area rapidly evolving it is essential for the practitioner to review drug prescribing information and recent literature to understand fully the impact of sex differences in clinical. Clopidogrel sold under the brand name Plavix among others is an antiplatelet medication used to reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke in those at high risk. Clinical pharmacokinetics is the application of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic principles to the safe and effective therapeutic management of an individual patient.
It has anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties and acts as an inhibitor of cyclooxygenase which results in the inhibition of the biosynthesis of prostaglandins. 1978 Nov625 Pt 2 Suppl867-72. Pharmacokinetics Compare the effectivenesss of oral and injectable drugs in randomized clinical trials Compare the cost of oral and injectable drugs.
Aspirin is a prodrug which is transformed into salicylate in the stomach in the intestinal mucosa in the blood and mainly in the liver. Some patient-related factors eg renal function genetic makeup sex age can be used to predict the pharmacokinetic parameters in populations. What is meant by non-linear pharmacokinetics.
The plasma concentration of the latter must be maintained within a relatively narrow range. The pharmacokinetic term half-life t12 refers to the time taken for half the initial dose of medicine administered to be eliminated from the body. It is rapidly hydrolyzed in the body to salicylic acid.
When the dose of a drug is increased we expect that the concentration at steady state will increase proportionately ie. Another example of altered absorption with increased gastric pH is early release of enteric-coated dosage forms eg enteric-coated aspirin enteric-coated erythromycin increasing the risk of gastrointestinal adverse effects. Drug transport across membranes For.
Aspirin also inhibits platelet aggregation and is used in the prevention of arterial and venous thrombosis. Outline Background Results Antibiotics Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs Vitamins. Clinical pharmacokinetics of aspirin Pediatrics.
Pharmacokinetics is the aspect of pharmacology dealing with how drugs reach their site of action and are removed from the body. According to its definition the volume of distribution abbreviated Vd is not a physical space. Literature review methods Medline Cochrane reviews Pharmacology textbook reviews Micromedex.
Details of pharmacokinetics are provided in the following sites in this work. Aspirin The prototypical analgesic used in the treatment of mild to moderate pain. Aspirin given shortly after a heart attack decreases the risk of death.
Aspirin Use Tied to Incident Heart Failure in At-Risk Adults. Aspirin Use Tied to Incident Heart Failure in At-Risk Adults. A Comparison of Coagulation Function in Patients Receiving Aspirin and Cefoperazone-Sulbactam With and Without Vitamin K 1.
T12 0693ke Where ke first order. Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat include Kawasaki disease pericarditis and rheumatic fever. However for some drugs the plasma drug.
Its effect starts about two hours after intake and lasts for five days. If the dose rate is increased or decreased say two-fold the plasma drug concentration will also increase or decrease two-fold. Pharmacokinetics refers to the movement and modification of medication inside the body.
It is also used together with aspirin in heart attacks and following the placement of a coronary artery stent dual antiplatelet therapy. Examples include ethanol phenytoin aspirin at high concentrations First order kinetics. The present analyses indicate that high doses of 500-1500 mg aspirin daily which are more gastrotoxic are no more effective than medium doses of 160-325 mgday or low doses of 75-150 mgday.
A Retrospective Observational Study. Or more simply its what the body does to this medication and how it does it. From Martindale The Extra.
Pharmacokinetics is the study of a drugs movements in the body and can be described as what the body does to the drug. Gastrointestinal intolerance to salicylate observed in some patients has. Volume of Distribution Fluid volume that would be required to contain the amount of drug present in the body at the same concentration as in the plasma Description.
Aspirin is very rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract when administered as a solution and somewhat more slowly when administered in tablets. Aspirin is also used long-term to help prevent further heart attacks ischaemic. Effectiveness of Various Dosages and Administration Methods of Tanezumab for the Treatment of Pain in Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis.