The electron beam behaves like a wavefront with wavelength about a million times shorter than lightwaves. Transmission Electron Microscope Uses in Microscopy Advantages and Disadvantages.

Transmission Electron Microscope Instrument Britannica
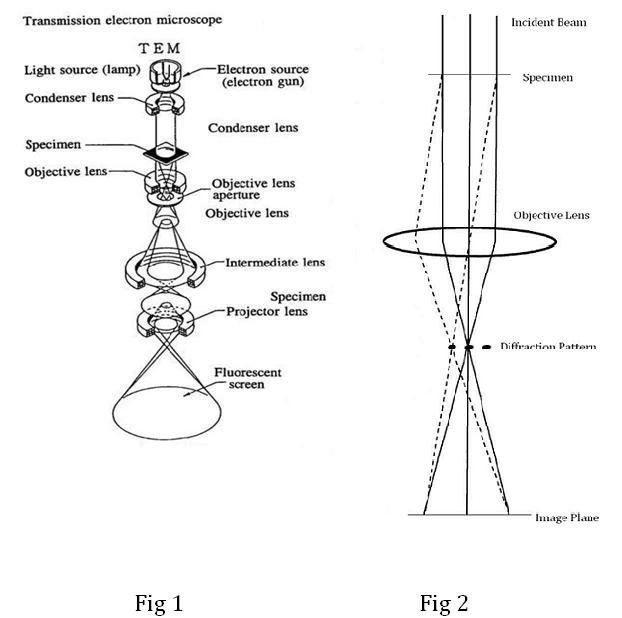
Working Principle of Electron microscope.

Working principle of transmission electron microscope. Transmission electron microscope. The major difference is the light microscope uses artificial light or natural light to create an image of the specimen. In order to get a better idea of just how small that is think of how small a cell is.
The transmission electron microscope TEM The scanning electron microscope SEM Principle of Electron Microscope. TEM Transmission electron microscopy. Working principle of Transmission Electron Microscope Electron Microscope follows the same principle as a light microscope follow.
Since the wavelength o f electrons are 100000 times shorter than visible light the electron microscopes have greater resolving power. 1 Transmission Electron Microscope TEM. Scanning transmission electron microscopy STEM combines the principles of transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy and can be performed on either type of instrument.
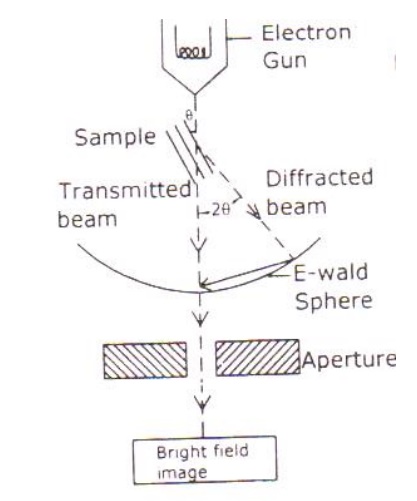
Electrons are made to pass through the specimen and the image is formed on the fluorescent screen either by using the transmitted beam or by using the diffracted beam. Guide Scanning Electron Microscopy Working Principle 8 Transmission electron microscopy TEM In TEM the accelerated electrons pass through the specimen. Working principle of TEM.
Like TEM STEM requires very thin samples and looks primarily at beam electrons transmitted by the sample. Microscopy Transmission electron microscopy TEM an abbreviation which can also stand for the instrument a transmission electron microscope is a microsco. The metal used in an electron microscope is tungsten.
TEMs produce high-resolution two-dimensional images allowing. There are two types of electron microscopes. Transmission Electron Microscopy In a conventional transmission electron microscope a thin specimen is irradiated with an electron beam of uniform current density.
Objective lens provides the formation of either. TEMs can magnify objects up to 2 million times. The electron gun generates electrons.
The transmitted ones then become focused as an enlarged image onto a fluorescent screen which. To familiarize the technique of sample preparation for transmission electron microscopy. Transmission electron microscopy TEM is the original form of electron microscopy and analogues to the optical microscope.
A high voltage current is applied which results in the excitation of the electrons in the form of a continuous stream that is used. In this microscope an electron beam from an electron gun is transmitted through an ultra-thin section of the microscopic object and the image is magnified by the electromagnetic fields. Electrons are made to pass through the specimen and the image is formed on the fluorescent screen either by using the transmitted beam or by using the diffracted beam.
TEM functions under the principle of optical microscopy. Transmission electron microscopes TEM are microscopes that use a particle beam of electrons to visualize specimens and generate a highly-magnified image. Under vacuum conditions the electron beam is accelerated by high pressure to form scattering electrons and transmission.
Electrons are emitted from the electron gun and illuminate the specimen through a two or three stage condenser lens system. Transmission electron microscope. At a maximum potential magnification of 1 nanometer TEMs are the most powerful microscopes.
A Transmission Electron Microscope TEM utilizes energetic electrons to provide morphologic compositional and crystallographic information on samples. The electrons are replaced by photons glass lenses are replaced by electromagnetic lenses and images are viewed in a screen instead of an eyepiece. Transmission electron microscopy principle and working lecture TEM - This microscopy lecture is going to explain the Transmission electron microscopy princ.
Electron microscopes use signals arising from the interaction of an electron beam with the sample to obtain information about structure morphology and composition. What is a Transmission Electron Microscope. Transmission electron microscopy uses high energy electrons up to 300 kV accelerating voltage which are accelerated to nearly the speed of light.
Electron beams are used in electron microscope to illuminate the specimen and thus creates an image. A transmission electron microscope TEM is a special type of microscope that uses electrons to create a magnified image up to a million times. It can achieve a resolution.
Transmission electron microscope that is transmission electron microscope is usually called electron microscope or electron microscope EM is the most widely used class of electron microscope. Two sets of condenser lenses focus the electron beam on the specimen and then into a thin tight beam.
Transmission Electron Microscope Principle Construction Working Advantages And Disadvantages

Figure 12 These Schematic Illustrations Compare The Components Of Transmission Electron Microscopes And S Microbiology Scanning Electron Microscope Microscopy

How Scanning Electron Microscopes Work In 2021 Scanning Electron Microscope Electron Microscope Microscopic
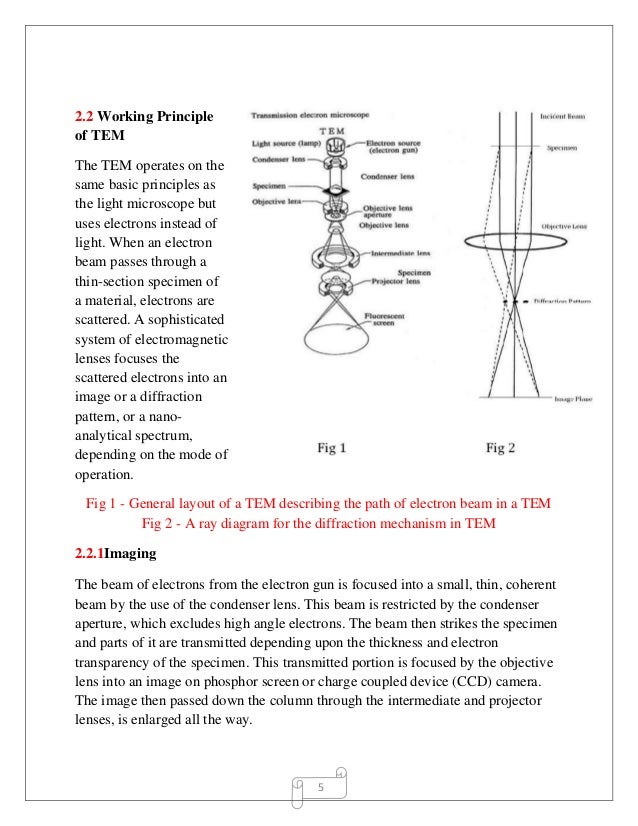
Principle Applications Of Transmission Electron Microscopy Tem

Schematic Diagram Of A Transmission Electron Microscope B Scanning Electron Microscope Scanning Electron Microscope Electron Microscope Microscopic Images
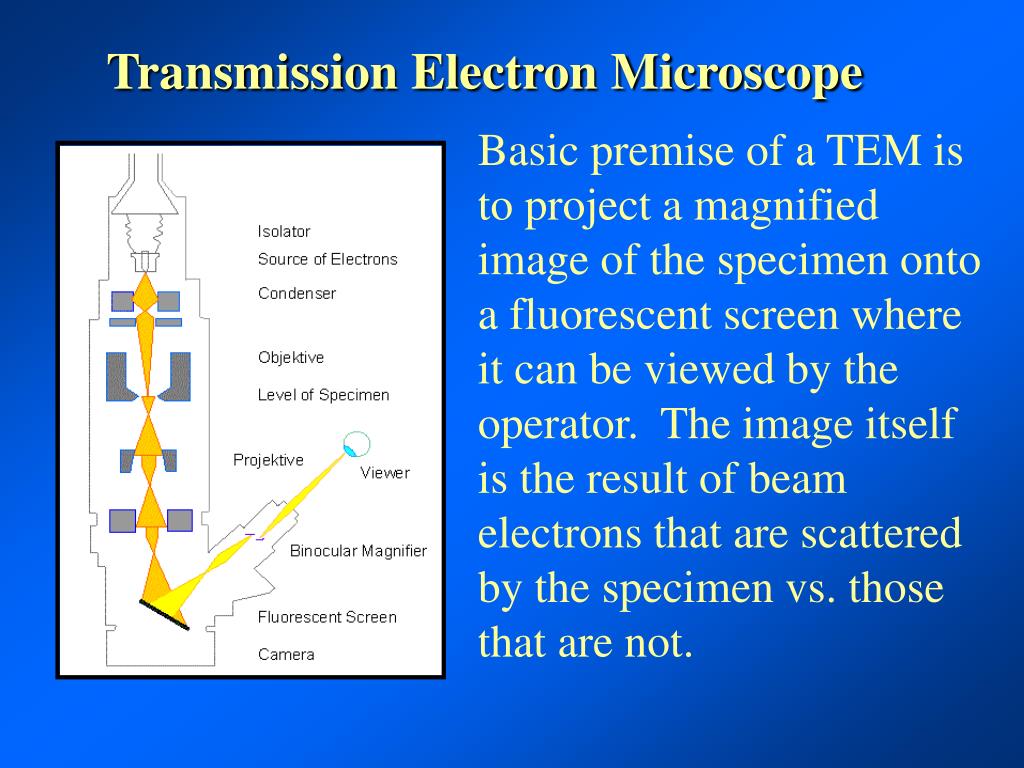
Ppt Transmission Electron Microscope Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6696605

How Does Sem Works Electron Microscope Scanning Electron Microscope Electrons

Basic Principle Of Transmission Electron Microscopy Tem Download Scientific Diagram
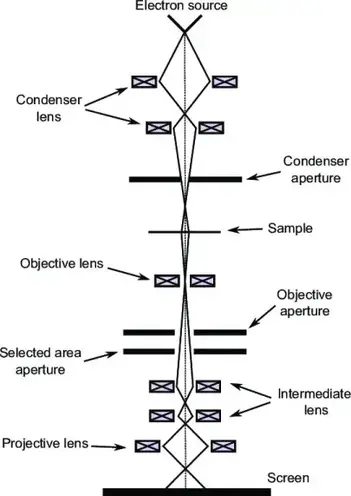
Electron Microscope Principle Types Applications Microbe Online