The potassium ion is the principal intracellular cation of most body tissues. Most potassium minerals are found in igneous rocks and are sparingly soluble.
Because this property leads to a cathartic action phosphate salts are employed as mild.

Potassium chloride mechanism of action. Potassium is the major cation of intracellular fluid and is essential for the conduction of nerve impulses in heart brain and skeletal muscle. Sodium and chloride major electrolytes of the fluid compartment outside of cells ie extracellular work together to control extracellular volume and blood pressure. This agent has potential antihypertensive effects and when taken as a nutritional.
14 131 172 If potassium is supplied but chloride is not alkalosis cannot be corrected. The transmission of nerve impulses. The carbonyl oxygens are strongly electro-negative and cation-attractive.
Increased plasma potassium levels reflecting dietary intakes are. If the ion is introduced into the intestine the absorbed phosphate is rapidly excreted. Mechanism of Action.
Absorption of sodium in the small intestine plays an important role in. In addition one ion can bind in the cavity at a site called SC or one or more ions at the extracellular side at more or less. Mechanism of Action.
In fact isolated potassium deficiency in dogs leads to mild metabolic acidosis. The potassium ion K is the principal intracellular cation of most body tissues. The mechanism of.
Potassium has several purported mechanisms of action for its antihypertensive effects. Pharmacology Mechanism of Action. Potassium maintains intracellular tonicity is required for nerve conduction cardiac skeletal and smooth muscle contraction production of energy the synthesis of nucleic acids maintenance of blood pressure and normal renal function.
There are however other minerals such as sylvite potassium chloride sylvinite a mixture of potassium and sodium chloride and carnallite potassium magnesium chloride that are found in deposits formed by evaporation of old seas or lakes. It was first isolated from potash the ashes of plants from which its name derives. Potassium transport through the hydrophobic interior of a cell membrane may be facilitated by several naturally occurring compounds that form lipid-soluble alkali metal cation.
The filter can accommodate potassium ions at 4 sites usually labelled S1 to S4 starting at the extracellular side. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. In animals the maintenance of normal cell volume and pressure is dependent on Na and K pumping 17.
Potassium Chloride is a metal halide composed of potassium and chloride. Mechanisms of action. Disturbances in sodium concentrations in the extracellular fluid are associated with disorders of water balance.
35 36 When potassium retention is prevented but sodium chloride is supplied alkalosis is corrected despite a persisting potassium deficit. Potassium K is the principal cation modulating the osmotic balance of the body fluids. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force.
Patients using drugs with extensive anticholinergic effects should avoid concomitant use with solid oral dosage forms of potassium chloride. Potassium preparations are used for supplementing potassium in order to treat or prevent low potassium levels in the blood hypokalemiaPotassium is a major mineral electrolyte that is important for the function of every cell in the bodyFor example it is important in. 60 In these scenarios after large meals insulin release and stimulation of Na K -ATPase are invariable.
May use effervescent potassium preparations. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to form flaky white potassium peroxide in only seconds of exposure. Potassium ions participate in a number of essential physiological processes including the maintenance of intracellular tonicity the transmission of nerve impulses the contraction of cardiac skeletal and smooth muscle and the maintenance of normal renal function.
The contraction of cardiac skeletal and smooth muscle. The mechanism of potassium channel selectivity remains under continued debate. On the other hand a large inhibition of.
This effect does not persist so it cannot explain the long-term effects on blood pressure. 130 Administration of potassium chloride leads to complete correction of both. It is also important to remember that nerve cells are surrounded by a membrane that allows some ions to pass through and blocks the passage of other ions.
And the maintenance of normal renal function. Potassium decreases intravascular volume partly through decreased sodium reabsorption ie increased urinary sodium excretion. If large amounts are given by this route much of it may escape absorption.
There are also some negatively charged protein molecules. Maintenance of normal renal function acid-base balance carbohydrate metabolism and gastric secretion. Explore the role of thirst in how the kidneys regulate electrolytes electrolyte deficiency.
Potassium is a chemical element with the symbol K from Neo-Latin kalium and atomic number 19. The important ions in the nervous system are sodium and potassium both have 1 positive charge calcium has 2 positive charges and chloride has a negative charge -. The metal is difficult to obtain from these minerals.
Electrolytes like sodium potassium and chloride are ions that help regulate the bodys fluid balance. 97 Mechanism of Action. Contraction of cardiac skeletal and smooth muscles.
Potassium ions participate in a number of essential physiological processes including the maintenance of intracellular tonicity. Once phosphate gains access to the body fluids and tissues it exerts little pharmacological effect. Inward-rectifying potassium channels allow more inward than outward potassium fluxes when open.
In rural China where villagers develop symptoms after ingestion of a large amount of food contaminated with barium chloride.

Potassium Chloride An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Regulation Of Smooth Muscle Calcium Sensitivity Kcl As A Calcium Sensitizing Stimulus American Journal Of Physiology Cell Physiology

Potassium Homeostasis And Management Of Dyskalemia In Kidney Diseases Conclusions From A Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes Kdigo Controversies Conference Kidney International
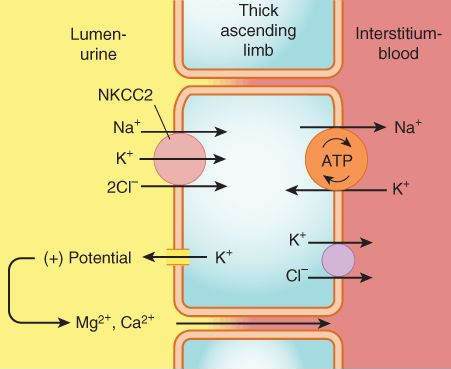
Diuretic Agents Basicmedical Key

The Mode Of Action Of Potassium Chloride On Muscles Journal Of Pharmacology And Experimental Therapeutics

Potassium Chloride And Patient Safety

Electrolyte Balance Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Mechanism Of Action Of Drugs For Hyperkalemia C Calcium H Hydrogen Download Scientific Diagram

The Effect Of High Potassium On The Endothelium And Smooth Muscle Download Scientific Diagram