For this type of reaction to occur the reduction potential of the reactant receiving the electrons must be lower than the reduction potential of the reactant giving up electrons. Cadmium hydroxide CdOH 2 2510 14.

How To Write The Formula For Copper Ii Bicarbonate Youtube
The copper metal reacts with oxygen resulting in the formation of an outer layer of.
Copper hydrogen carbonate. MercuryI Hg 2 2. Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu from Latin. CaSO4 calcium sulfate 5.
Ionic bonds are atomic bonds created by the attraction of two differently charged ionsThe bond is typically between a metal and a non-metal. Calcium hydroxide CaOH 2 5. Cuprum and atomic number 29.
Copper will not react with hydrochloric acid. Hydrogen storage requires the reduction of an enormous volume of gas and an objective in hydrogen storage is to pack hydrogen as close as possible ie. FeC2H3O22 iron II acetate 4.
And blocks inositol. Answer 1 of 25. FeNO22 iron II nitrite 9.
Cu 2 OH 2. SnSO4 tin II sulfate 14. Cu2CO3 copper I carbonate 8.
At the same time fluctuations in the levels of iron and zinc which are essential elements were determined in the tissuesLevels of copper iron and zinc in blood were. Calcium hydrogen phosphate CaHPO 4 110 7. Hydroxide ions from say sodium hydroxide solution remove hydrogen ions from the water ligands attached to the copper ion.
Cu 2 OH. Cadmium sulfide CdS 810 28. If the atmosphere consists of high humidity moisture then this process is faster.
Water Hydrogen sulfate Hydrogen phosphate Hydrogen nitrate. This is our newest publication and has been created to support the school technician profession in Scotland. BaClO42 barium perchlorate 11.
Rats were fed a diet contain basic cupric carbonate at doses of 0 70 220 670 and 2000 ppm as cupric hydroxide and 12 months the levels of copper in the blood and tissues were determined by atomic absorption analysis. NO 2 Potassium. Ionic bonds also melt at high temperatures.
As a mineral it is known as tenoriteIt is a product of copper mining and the precursor to many other copper-containing products and chemical compounds. 1 Cs ion and 1 HCO 3-ion. Cadmium oxalate CdC 2 O 4 1510 8.
K2Cr2O7 potassium dichromate 6. Oxidation is a phenomenon whereby an element loses electrons andor hydrogen on interacting with another element. Copper sulphate blue stone blue vitriol are all common names for pentahydrated cupric sulphate CuSO 4 5H 2 O which is the best known and the most widely used of the copper salts.
ZnHCO32 zinc bicarbonate 15. Carbonate Iron II hydroxide Iron II sulfate Iron II phosphate Iron II nitrate Mg2Magnesium chloride Magnesium carbonate Magnesium hydroxide Magnesium sulfate Magnesium phosphate Magnesium nitrate HHydrogen chloride Hydrogen carbonate. CdOH2 cadmium hydroxide 13.
Indeed it is often the starting raw material for. The chemical element Calcium Ca atomic number 20 is the fifth element and the third most abundant metal in the earths crust. Calcium chromate CaCrO 4 7110 4.
It is a soft malleable and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivityA freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange colorCopper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity as a building material and as a constituent of various metal alloys such as sterling. The formula unit for the ionic compound cesium hydrogen carbonate consists of which of the following. 2 Cs ions and 1 CO 3 2-ion.
Lithium Carbonate is the carbonate salt of lithium a soft alkali metal with antimanic and hematopoietic activities. What is the correct formula unit for the ionic compound copperII hydroxide. AgNO3 silver nitrate 10.
Uses of Copper Sulphate. To increase the density of hydrogen either work must be applied to compress the gas or the temperature must be decreased below the critical. H 3 O LeadII Pb 2.
H 3 O hydronium. Lithium interferes with transmembrane sodium exchange in nerve cells by affecting sodium potassium-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase Na K-ATPase. 2 Cs ions and 1 HCO 3 2-ion.
Why and why does this reaction even involve electron. Copper oxide is a base. Optical constants of Cu Copper Johnson and Christy 1972.
Calcium fluoride CaF 2 5310 9. This activity includes every compound formula and name that can be formed from the list 44 Ions provided in Chemistry A at Pickerington High School Central. 1 Cs 2 ion and 2 HCO 3-ions.
Alters the release of neurotransmitters. CopperI Cu 2 copperII Polyatomic positive ions often have common names ending with the suffix -onium. A black solid it is one of the two stable oxides of copper the other being Cu 2 O or copperI oxide cuprous oxide.
Carbonate CO3 2-chlorate ClO3-chlorite ClO2-chromate CrO4 2-cyanide CN-dichromate Cr2O7 2-hydrogen carbonate bicarbonate HCO3-hydrogen sulfate bisulfate HSO4-hydrogen phosphate biphosphate HPO4 2-hydroxide OH-hypochlorite ClO- iodate IO3-nitrate. H aq OH-aq H 2 Ol Pure water is neutral. Calcium carbonate CaCO 3 2810 9.
Once a hydrogen ion has been removed from two of the water molecules you are left with a complex with no charge - a neutral complex. NH 4 ammonium. The metal is trimorphic harder than sodium but softer than aluminiumA well as beryllium and aluminium and unlike the alkaline metals it doesnt cause skin-burns.
It is less chemically reactive than alkaline metals and than the other alkaline-earth. The structure of the bond is rigid strong and often crystalline and solid. 1 Cs 2 ion and 1 CO 3 2-ion.
Similar to iron and aluminum the element copper undergoes the process of oxidation if it is exposed to air. Cu H 2 O 2 CuO H 2 O CuO 2HCl CuCl 2 H 2 O Uses. KHCO3 potassium bicarbonate 7.
Affects cyclic adenosine monophosphate concentrations. Hydrogen carbonate HCO 3 1 sulfite SO 2 2 lithium Li 1 bisulfate hydrogen sulfate HSO 4 1 sulfide S 2 2 nickelII nickelous Ni 2 2 bromate BrO 3 1 thiocyanate SCN 1 potassium K 1 bromide Br 1 thiosulfate S 2 O 3 2 2 A note. In acid-alkali neutralisation reactions hydrogen ions from the acid react with hydroxide ions from the alkali.
Cadmium carbonate CdCO 3 5210 12. TinIV Sn 4. CopperII oxide or cupric oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CuO.
PbCO32 lead II carbonate 12. We will be publishing Issue 1 of The School STEM Technician at noon on the 1st December 2021 via the SSERC website. Negative ions that consist of a single atom are named by adding the suffix -ide to the stem of the name of the element.
To reach the highest volumetric density using as little additional material and energy as possible. Cu2CO3 copper I carbonate 3. It can also be made by reacting copperII hydroxide copperII oxide or copperII carbonate with hydrochloric acid and from pure copper and from 11 solution of hydrogen peroxide and hydrochloric acid where copper first get oxidized to CuO from H2O2 and then reacts with HCl to form CuCl2 reaction goes like this.
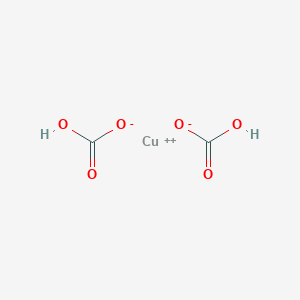
Copper 2 Bis Hydrogen Carbonate C2h2cuo6 Chemspider

Ionic Compounds Names And Formulas Naming Compounds In Chemistry Is Called Nomenclature Ppt Download

How To Write The Formula For Copper Ii Bicarbonate Youtube
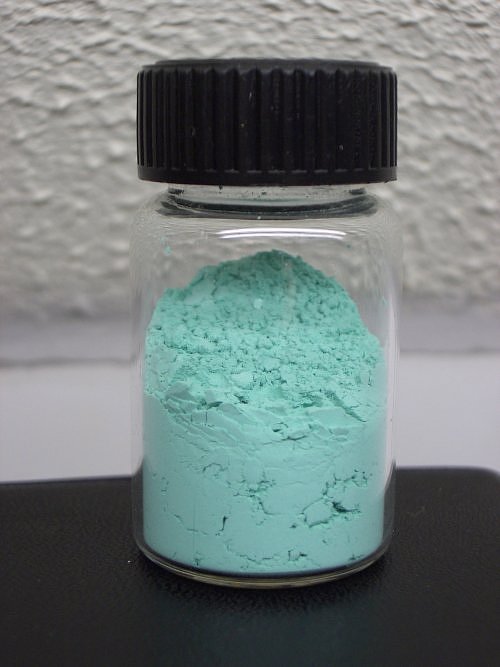

Basic Copper Carbonate Wikipedia
Copper Hydrogen Carbonate C2h2cuo6 Pubchem
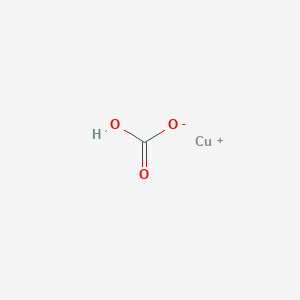
Copper 1 Hydrogen Carbonate Chcuo3 Chemspider
Copper 1 Hydrogen Carbonate Chcuo3 Pubchem

Ionic Compounds Names And Formulas Naming Compounds In
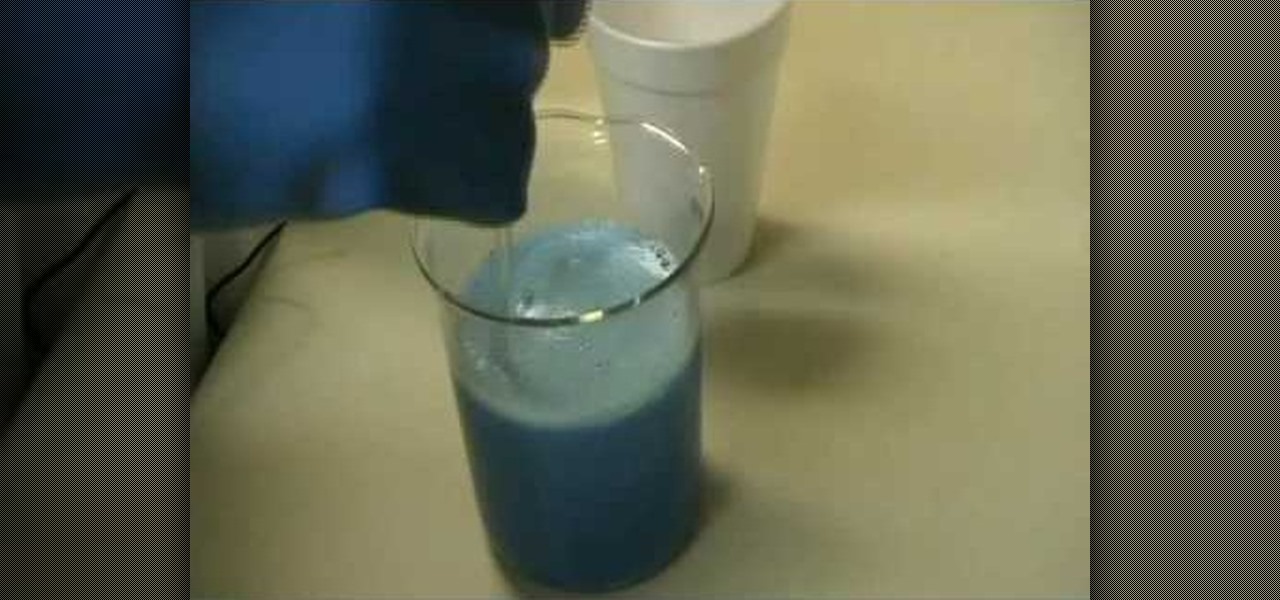

How To Synthesize Copper Ii Carbonate Sodium Bicarbonate Science Experiments Wonderhowto